November 18, 2025
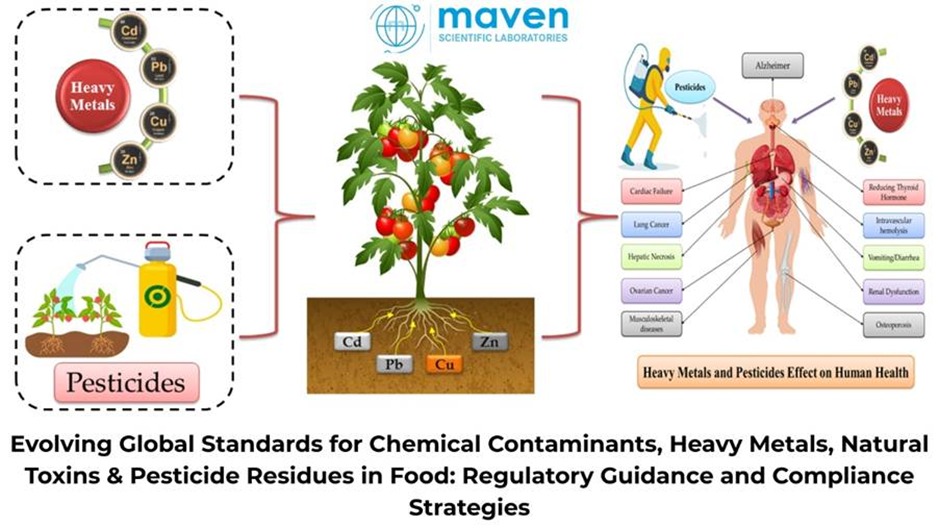
Ensuring food safety remains a critical global public health priority, especially as supply chains expand and environmental conditions continue to shift. Regulatory bodies, including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), have established strict requirements to monitor and manage chemical contaminants, heavy metals, naturally occurring toxins, process contaminants, and pesticide residues in the food system. For food manufacturers, importers, and distributors, maintaining compliance is not just regulatory—it is reputational, operational, and consumer-trust driven.
At Maven Regulatory Solutions, we support food and nutraceutical companies in navigating evolving regulatory expectations, ensuring proactive risk mitigation and robust product compliance across domestic and international markets.
Understanding the FDA Framework for Contaminant & Pesticide Control
The FDA’s regulatory oversight involves:
|
Category |
Source |
Examples |
Regulatory Control |
|
Chemical Contaminants |
Environmental, manufacturing, packaging |
PFAS, Dioxins, Benzene |
Action Levels / Guidance Levels |
|
Heavy Metals |
Soil, water, agricultural inputs |
Arsenic, Lead, Cadmium, Mercury |
Risk-based action and testing guidance |
|
Natural Toxins |
Plants, fungi, marine organisms |
Mycotoxins, Hypoglycin A, Microcystis |
Compliance Policies & maximum levels |
|
Process Contaminants |
Heat processing / production |
Acrylamide, 4-MEI, Glycidyl Esters |
Industry guidance on reduction |
|
Pesticide Residues |
Agricultural use |
Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides |
EPA-set tolerance limits |
Food manufacturers are legally required to implement Preventive Controls for Chemical Hazards under the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA).
Key Regulatory Guidance Documents: Current Landscape
1. Chemical Contaminants
- Acrylamide: Guidance for Industry on reduction in processed foods
- Dioxins & PCBs: Recommended contamination assessments
- Melamine: Industry guidance to prevent adulteration
- Radionuclides: Compliance Policy Guides for domestic & imported foods
2. Heavy Metals
- Arsenic: Action levels set for apple juice and infant rice cereal
- Lead: 2025 action levels for processed foods intended for infants and children
- Cadmium & Mercury: Risk-based surveillance in fish and grains
3. Natural Toxins
- Mycotoxins: FDA advisory levels in grains, nuts, and animal feed
- Hypoglycin A: Compliance policy for ackee-containing products
- Patulin: Guidance for apple juice and related products
4. Pesticide Residues
The EPA determines legal tolerance limits. FDA enforces compliance through sampling, testing, import surveillance, and targeted investigations.
Why This Matters Now: Increased Regulatory Scrutiny
- Growing concern about food safety in early-childhood nutrition
- Expanded FDA focus on contaminants affecting cognitive development
- Enhanced testing initiatives on school meals, public nutrition programs, and imported foods
- Rising recall and public safety alerts tied to non-compliance with contaminant limits
Global food brands are now expected not just to comply—but to demonstrate proactive risk control.
How Maven Regulatory Solutions Supports Compliance
At Maven Regulatory Solutions, we provide:
- Regulatory Strategy & Compliance Roadmaps
- FSMA Preventive Controls Program Development
- Food Contaminant & Pesticide Risk Assessments
- Labelling & Product Claims Compliance
- Supplier Qualification & Global Supply Chain Risk Mitigation
- Preparation for FDA Inspections and Import Oversight
Our approach ensures audit-ready documentation, lower compliance risk, and safer market access.
Conclusion
With increasing global awareness of chemical and environmental contaminants in food, regulatory expectations continue to evolve. Organizations that adopt a preventive, data-driven approach to food safety will not only avoid regulatory setbacks but also strengthen consumer trust and market resilience.
Maven Regulatory Solutions remains committed to supporting the food and nutraceutical industry in navigating this shifting regulatory landscape through expert guidance, compliance management, and continuous improvement frameworks.

Post a comment